Diodes Remains On Reverse Bias . — reverse bias: This characteristic is used in voltage regulation circuits. — explore the key differences between forward bias and reverse bias in semiconductor diodes and learn how their. — reverse bias is important in zener diodes because it allows them to operate in the breakdown region, while maintaining a constant voltage across the diode. — a diode in reverse bias must be added across output terminals of each power supply. Intrinsic concentration would increase with increase in temperature and hence minority charges would increase with. — understanding forward bias vs reverse bias configurations in diodes, exploring the theoretical aspects, implementation, applications, and considerations while noting the key differences between forward bias vs reverse bias When the voltage on the n side is higher than the voltage on the p side, we say the diode is under reverse bias.
from electric-shocks.com
When the voltage on the n side is higher than the voltage on the p side, we say the diode is under reverse bias. — understanding forward bias vs reverse bias configurations in diodes, exploring the theoretical aspects, implementation, applications, and considerations while noting the key differences between forward bias vs reverse bias — reverse bias is important in zener diodes because it allows them to operate in the breakdown region, while maintaining a constant voltage across the diode. This characteristic is used in voltage regulation circuits. — a diode in reverse bias must be added across output terminals of each power supply. — reverse bias: Intrinsic concentration would increase with increase in temperature and hence minority charges would increase with. — explore the key differences between forward bias and reverse bias in semiconductor diodes and learn how their.
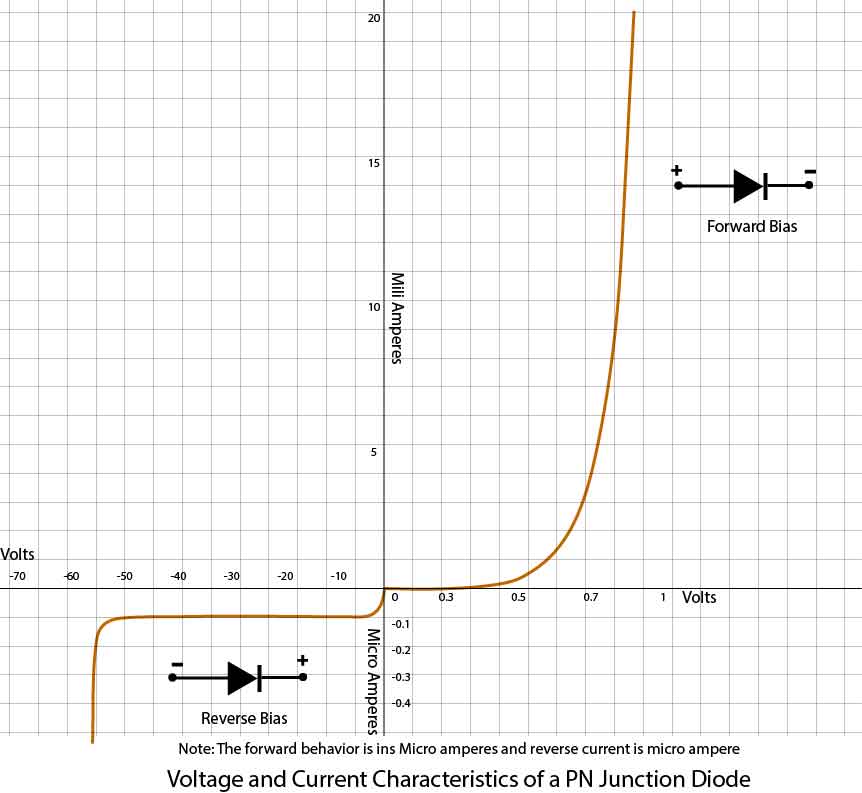
Forward Bias Diode and Reverse Bias Diode Characteristic Graph
Diodes Remains On Reverse Bias — explore the key differences between forward bias and reverse bias in semiconductor diodes and learn how their. — understanding forward bias vs reverse bias configurations in diodes, exploring the theoretical aspects, implementation, applications, and considerations while noting the key differences between forward bias vs reverse bias — explore the key differences between forward bias and reverse bias in semiconductor diodes and learn how their. Intrinsic concentration would increase with increase in temperature and hence minority charges would increase with. This characteristic is used in voltage regulation circuits. When the voltage on the n side is higher than the voltage on the p side, we say the diode is under reverse bias. — a diode in reverse bias must be added across output terminals of each power supply. — reverse bias: — reverse bias is important in zener diodes because it allows them to operate in the breakdown region, while maintaining a constant voltage across the diode.
From www.researchgate.net
Measured CV characteristics versus reverse bias for diodes of various Diodes Remains On Reverse Bias — explore the key differences between forward bias and reverse bias in semiconductor diodes and learn how their. — understanding forward bias vs reverse bias configurations in diodes, exploring the theoretical aspects, implementation, applications, and considerations while noting the key differences between forward bias vs reverse bias When the voltage on the n side is higher than the. Diodes Remains On Reverse Bias.
From binaryupdates.com
What is Diode Diodes Remains On Reverse Bias — reverse bias is important in zener diodes because it allows them to operate in the breakdown region, while maintaining a constant voltage across the diode. — reverse bias: — understanding forward bias vs reverse bias configurations in diodes, exploring the theoretical aspects, implementation, applications, and considerations while noting the key differences between forward bias vs reverse. Diodes Remains On Reverse Bias.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Biasing Modes for Diodes PowerPoint Presentation, free download Diodes Remains On Reverse Bias Intrinsic concentration would increase with increase in temperature and hence minority charges would increase with. When the voltage on the n side is higher than the voltage on the p side, we say the diode is under reverse bias. — reverse bias is important in zener diodes because it allows them to operate in the breakdown region, while maintaining. Diodes Remains On Reverse Bias.
From www.electronicsplanet.ch
Diode in forward and reverse bias Diodes Remains On Reverse Bias — understanding forward bias vs reverse bias configurations in diodes, exploring the theoretical aspects, implementation, applications, and considerations while noting the key differences between forward bias vs reverse bias When the voltage on the n side is higher than the voltage on the p side, we say the diode is under reverse bias. — reverse bias is important. Diodes Remains On Reverse Bias.
From electronics.stackexchange.com
Multiple diodes in series reverse biased Electrical Engineering Stack Diodes Remains On Reverse Bias — reverse bias: — explore the key differences between forward bias and reverse bias in semiconductor diodes and learn how their. — a diode in reverse bias must be added across output terminals of each power supply. — understanding forward bias vs reverse bias configurations in diodes, exploring the theoretical aspects, implementation, applications, and considerations while. Diodes Remains On Reverse Bias.
From www.arrow.com
What is Diode Biasing? Forward & Reverse Bias Diodes Explained Arrow Diodes Remains On Reverse Bias — explore the key differences between forward bias and reverse bias in semiconductor diodes and learn how their. — reverse bias: Intrinsic concentration would increase with increase in temperature and hence minority charges would increase with. — a diode in reverse bias must be added across output terminals of each power supply. — reverse bias is. Diodes Remains On Reverse Bias.
From instrumentationtools.com
Forward Bias & Reverse Bias Diode Working Animation Inst Tools Diodes Remains On Reverse Bias Intrinsic concentration would increase with increase in temperature and hence minority charges would increase with. — a diode in reverse bias must be added across output terminals of each power supply. — understanding forward bias vs reverse bias configurations in diodes, exploring the theoretical aspects, implementation, applications, and considerations while noting the key differences between forward bias vs. Diodes Remains On Reverse Bias.
From www.solveforum.com
[Solved] Applying voltage across reversebiased diode SolveForum Diodes Remains On Reverse Bias — reverse bias is important in zener diodes because it allows them to operate in the breakdown region, while maintaining a constant voltage across the diode. — understanding forward bias vs reverse bias configurations in diodes, exploring the theoretical aspects, implementation, applications, and considerations while noting the key differences between forward bias vs reverse bias Intrinsic concentration would. Diodes Remains On Reverse Bias.
From www.sarthaks.com
Of the diodes shown in the following diagrams, which one is reverse Diodes Remains On Reverse Bias — reverse bias is important in zener diodes because it allows them to operate in the breakdown region, while maintaining a constant voltage across the diode. — understanding forward bias vs reverse bias configurations in diodes, exploring the theoretical aspects, implementation, applications, and considerations while noting the key differences between forward bias vs reverse bias — explore. Diodes Remains On Reverse Bias.
From mavink.com
Zener Diode Reverse Bias Circuit Diagram Diodes Remains On Reverse Bias When the voltage on the n side is higher than the voltage on the p side, we say the diode is under reverse bias. This characteristic is used in voltage regulation circuits. Intrinsic concentration would increase with increase in temperature and hence minority charges would increase with. — explore the key differences between forward bias and reverse bias in. Diodes Remains On Reverse Bias.
From electric-shocks.com
Forward Bias Diode and Reverse Bias Diode Characteristic Graph Diodes Remains On Reverse Bias — a diode in reverse bias must be added across output terminals of each power supply. — understanding forward bias vs reverse bias configurations in diodes, exploring the theoretical aspects, implementation, applications, and considerations while noting the key differences between forward bias vs reverse bias — explore the key differences between forward bias and reverse bias in. Diodes Remains On Reverse Bias.
From dxomocnrg.blob.core.windows.net
Zener Diode Functions In Forward And Reverse Bias at Donnie Burke blog Diodes Remains On Reverse Bias This characteristic is used in voltage regulation circuits. Intrinsic concentration would increase with increase in temperature and hence minority charges would increase with. When the voltage on the n side is higher than the voltage on the p side, we say the diode is under reverse bias. — reverse bias: — reverse bias is important in zener diodes. Diodes Remains On Reverse Bias.
From www.youtube.com
PNJunction Diode Reverse Bias Characteristics YouTube Diodes Remains On Reverse Bias — a diode in reverse bias must be added across output terminals of each power supply. — explore the key differences between forward bias and reverse bias in semiconductor diodes and learn how their. This characteristic is used in voltage regulation circuits. — reverse bias: — reverse bias is important in zener diodes because it allows. Diodes Remains On Reverse Bias.
From theorycircuit.com
Zener diode tutorial Diodes Remains On Reverse Bias — reverse bias is important in zener diodes because it allows them to operate in the breakdown region, while maintaining a constant voltage across the diode. When the voltage on the n side is higher than the voltage on the p side, we say the diode is under reverse bias. Intrinsic concentration would increase with increase in temperature and. Diodes Remains On Reverse Bias.
From electronicsideas.com
A simplified explanation of How diodes work Electronics Ideas Diodes Remains On Reverse Bias — reverse bias: This characteristic is used in voltage regulation circuits. When the voltage on the n side is higher than the voltage on the p side, we say the diode is under reverse bias. — reverse bias is important in zener diodes because it allows them to operate in the breakdown region, while maintaining a constant voltage. Diodes Remains On Reverse Bias.
From www.circuitbread.com
Diodes and Diode Circuits Study Guides CircuitBread Diodes Remains On Reverse Bias When the voltage on the n side is higher than the voltage on the p side, we say the diode is under reverse bias. Intrinsic concentration would increase with increase in temperature and hence minority charges would increase with. — a diode in reverse bias must be added across output terminals of each power supply. This characteristic is used. Diodes Remains On Reverse Bias.
From www.wevolver.com
Forward Bias, Reverse Bias and their effects on Diodes Diodes Remains On Reverse Bias When the voltage on the n side is higher than the voltage on the p side, we say the diode is under reverse bias. — reverse bias: — explore the key differences between forward bias and reverse bias in semiconductor diodes and learn how their. Intrinsic concentration would increase with increase in temperature and hence minority charges would. Diodes Remains On Reverse Bias.
From electric-shocks.com
Forward Bias Diode and Reverse Bias Diode Characteristic Graph Diodes Remains On Reverse Bias — explore the key differences between forward bias and reverse bias in semiconductor diodes and learn how their. — understanding forward bias vs reverse bias configurations in diodes, exploring the theoretical aspects, implementation, applications, and considerations while noting the key differences between forward bias vs reverse bias This characteristic is used in voltage regulation circuits. — reverse. Diodes Remains On Reverse Bias.